Live Tides
NOTICES TO MARINERS
Charts & Surveys
Incident reporting
Life-threatening emergencies on the river:
Call 999 and ask for the Coastguard
For near miss, safety observations and incident reporting click below
PLA receives two nominations at the Maritime UK Awards 2025

We are delighted to share that we have been named as a finalist in two categories at the Maritime UK Awards 2025.
- Employer of the Year Award
- Rising Star Award for Emily McLean (Senior Technical Advisor)
Being named a finalist for Employer of the Year not only honours the progress we’ve made, but it also inspires us to continue raising the bar, supporting our strategic goals and the people who make them possible.
It is an honour to have our people focused values and exceptional employees recognised by the wider maritime industry. It is an affirmation of what we know - that we are dedicated to supporting and developing our people and that when our people make the most of opportunities in front of them, they thrive.
 Congratulations also to Emily McLean. This nomination is external validation of what we in the PLA already know, that she is a rising star whose career is going from strength-to-strength. The hard work and energy Emily puts into her role is incredible, and we are proud to see this recognised.
Congratulations also to Emily McLean. This nomination is external validation of what we in the PLA already know, that she is a rising star whose career is going from strength-to-strength. The hard work and energy Emily puts into her role is incredible, and we are proud to see this recognised.
Emily said: "I’m delighted to have been shortlisted for this award. Even being nominated means a great deal to me. Having work related to the environment receive the recognition it deserves is crucial for driving progress in the maritime industry.
"I would also like to thank all my colleagues in Environment and Sustainability, I couldn’t have achieved what I have without your support."
We look forward to 26 June to celebrate the achievements of the Maritime Industry in Dover with colleagues from across the industry.
Related content

Location: London/Gravesend Remuneration: £28,971 per annum for a commitment of up to 24 days per...


International Day for Women in Maritime 2025

Today, Sunday 18 May, is the International Day for Women in Maritime 2025.
Hear PLA colleagues reflect on what it’s like to be a woman in the Maritime Industry.
Rachel De Bont, Safety Training and Compliance Manager
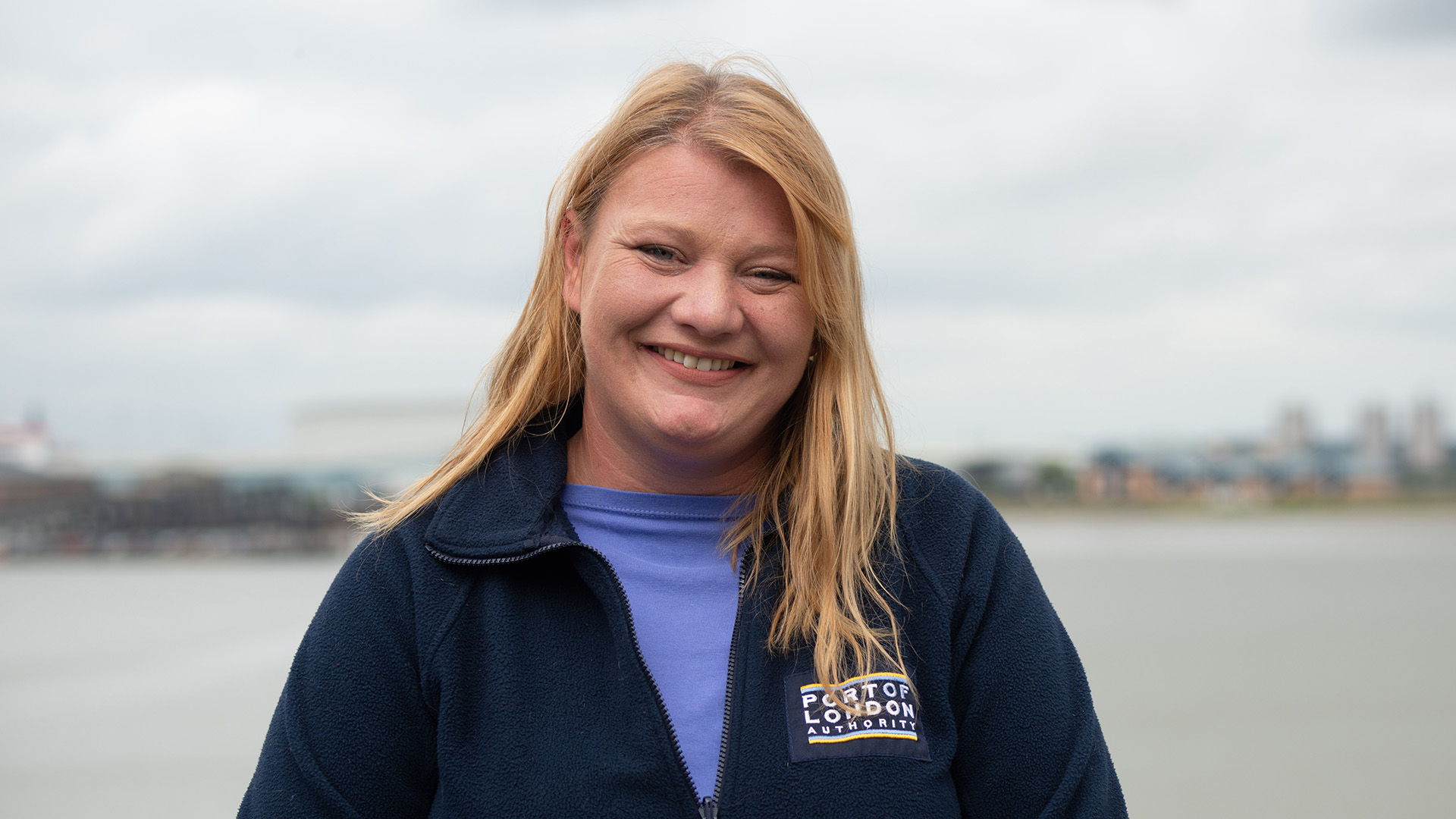 Rachel has worked at the PLA for 11 years in a variety of roles.
Rachel has worked at the PLA for 11 years in a variety of roles.
Q: What is it about working in the maritime industry that appeals to you?
A: There’s so much to love. Working afloat offers a unique sense of freedom. The complexity of marine navigation, seamanship is passed down through generations without road signs or roundabouts, continues to evolve alongside new technology and regulation. The skills gained at sea are incredibly versatile and have proven invaluable ashore.
Q: Do you have any career highlights you’d like to share?
A: Supporting the Boatmaster’s Apprenticeship scheme was a true highlight. Helping to shape a standard alongside Thames operators and training providers was incredibly rewarding. But nothing beats seeing the relief and pride on an apprentice’s face when they pass their oral exam - it's been a privilege to support them on their journey.
Q: Do you have any advice for women who want to enter the maritime industry?
A: Absolutely - do your research and take that first step! Follow others in the industry on platforms like Instagram and LinkedIn – a special mention to Captain Scarlett, one of our own, now an Officer of the Watch Unlimited, who documents her career openly. Explore opportunities like Tiller & Wheel’s free introductory sailing experiences on Thames Barges or speak with local boat clubs and operators to get a real sense of life on the water.
Q: Do you have any advice for overcoming challenges you may face in this industry as a woman?
A: Talk to others. The women I’ve worked with have always been open to sharing their experiences and advice. Chances are, someone’s faced the same challenge and can help steer you in the right direction.
Q: Do you have any women who are inspirational to you in your career?
Far too many to name just one – but if I had to pick three:
- My mum, who grew up on boats, never attended school, but went to university later in life overcoming many challenges – her determination showed me that anything is possible.
- Scarlett, our former apprentice, now a 3rd Officer at DFDS, whose drive and growth have inspired me to continue pushing forward.
- Lyn, our Harbour Master, who worked her way up from deckhand to Master Mariner while raising her beautiful family, she's incredible! Her resilience and leadership are a constant inspiration to me.
While it's International Women in Maritime Day, I’d also like to acknowledge the many men who have supported and mentored me throughout my journey. From my brother, who has been a constant source of strength, to the Head of Marine Services, who gave me my first opportunity back afloat after becoming a new mum, and the many managers and crews who have shared their knowledge and encouraged me to grow in my own way.
The maritime industry truly is unique – a global family where support often comes from all directions.
Odina Ifeoma, IT Service Delivery Manager
Emily Sawyer, Navigation Systems Co-ordinator
Danielle Spencer, Senior Health, Safety and Wellbeing Advisor
Related content

Location: London/Gravesend Remuneration: £28,971 per annum for a commitment of up to 24 days per...


New PLA Trainee Marine Pilots
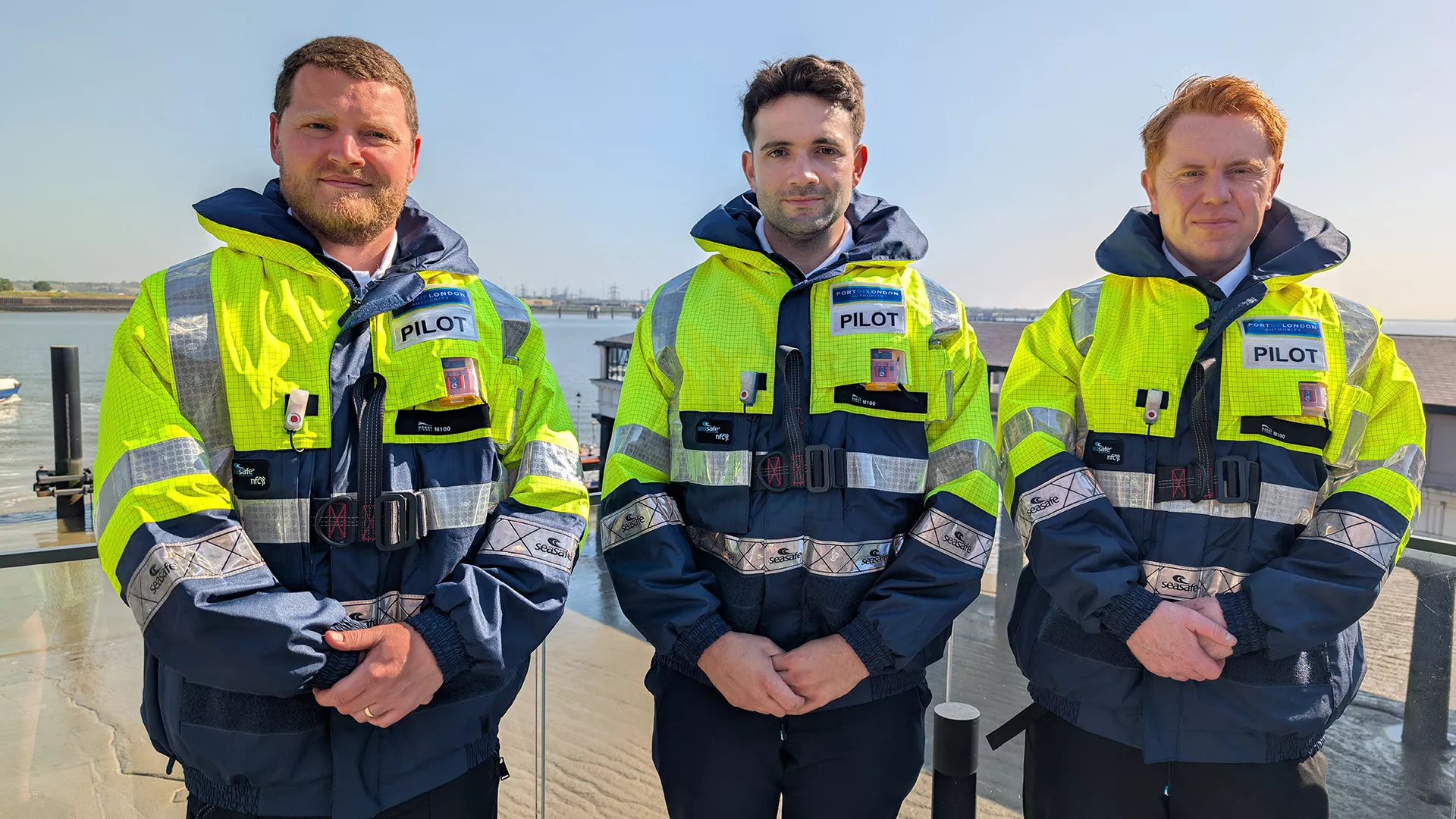

We’re delighted to welcome Lloyd, John and Alfie to the Port of London Authority as they begin their journey as trainee marine pilots. Each brings with them a wealth of experience, a deep commitment to maritime safety, and a shared passion for ship handling and navigation. The Thames is one of the most dynamic and challenging pilotage environments in the world, and we’re confident they will rise to the occasion.
Lloyd Mason
Originally from Dover, Lloyd Mason began his maritime career as a cadet with P&O Ferries, working on routes between Dover–Calais and Hull–Rotterdam. He spent four years as a Second Mate in Dover before moving to New Zealand, where he worked for eight years as Second Mate and two years as Chief Officer with Interislander. He also served as Mate for two months with the Shetland Islands ferries.
Lloyd has aspired to be a pilot since his cadetship. His decision to return to the UK was driven by a desire to be closer to family and spend more time with his children. He is particularly excited about the ship handling aspects of the role. Outside of work, he enjoys mountain biking and hiking.
John Cassidy
Originally from Liverpool, John Cassidy has over 15 years of experience in the marine industry. He has worked on a wide range of vessels including container ships, tankers, and most recently, tugs. Throughout his career, he has developed a strong and varied skill set, with becoming a PLA trainee pilot marking a proud milestone.
John sees pilotage as the pinnacle of a seafaring career—one that offers both challenge and immense job satisfaction. He is particularly excited about being a key part of the bridge team, working on a variety of vessels, and mastering ship handling on the Thames. Outside of work, John enjoys hiking, climbing, golf, reading, and travelling.
Alfie Gude
Originally from Grimsby, Alfie Gude has spent over 14 years in the maritime industry, working on a broad range of vessel types including ROPAX ferries, harbour tugs, tankers, dry bulk carriers, and RORO vessels across Australia and internationally. He has held roles from cadet through to Chief Officer and Relief Master, with particular strengths in ship handling, crisis management, and safety leadership.
Alfie has also worked as a maritime safety consultant for major clients including BHP, Rio Tinto, and the Australian Antarctic Division. Drawn to the unique challenges of the Thames, he sees pilotage with the PLA as a professional milestone. He is excited to join a world-class team and continue developing his skills in one of the most demanding pilotage environments. Outside of work, Alfie enjoys rugby, road cycling, clay target shooting, and spending time outdoors with his wife and children.
Related content

Location: London/Gravesend Remuneration: £28,971 per annum for a commitment of up to 24 days per...



Our commitments
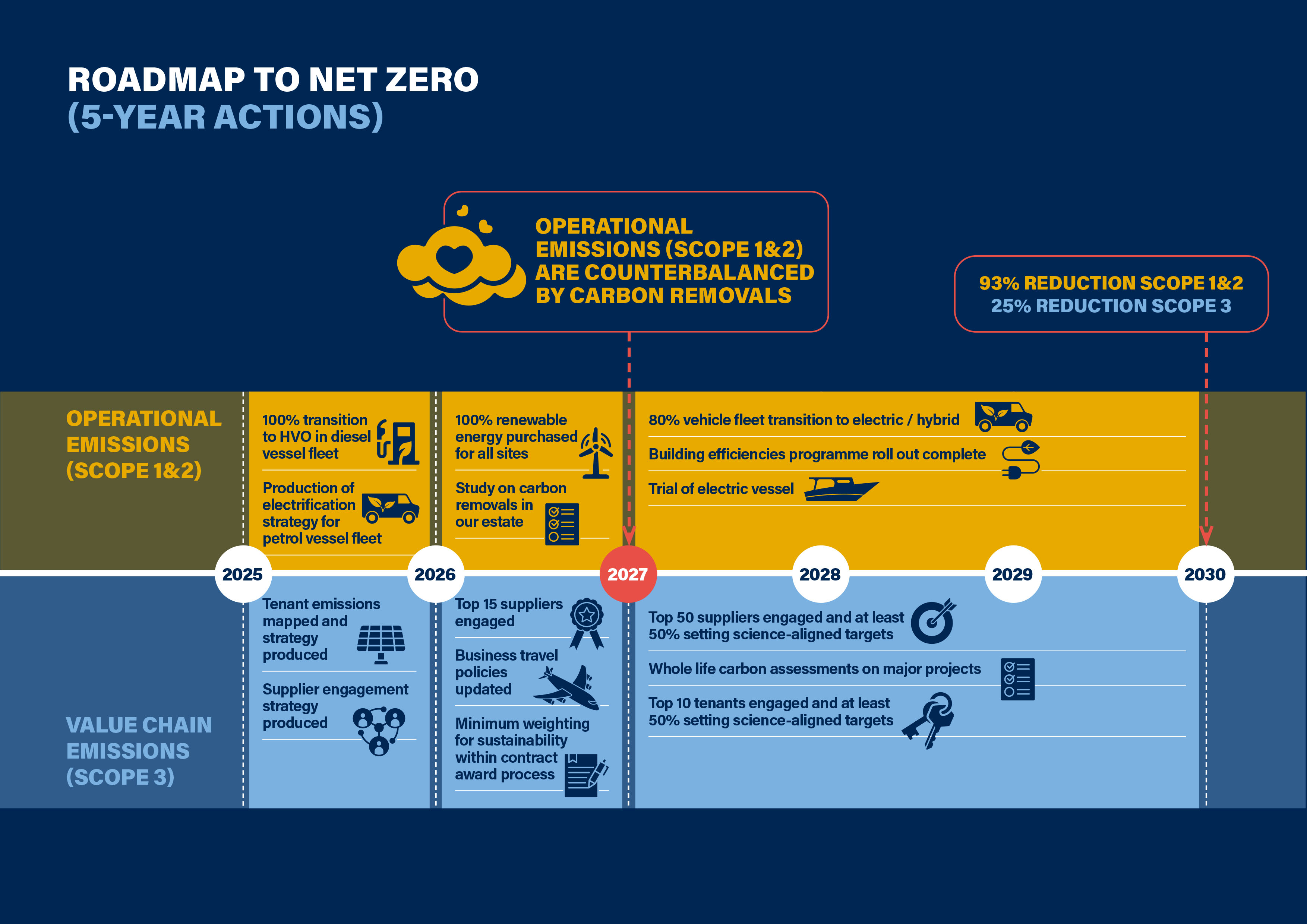
-Operational emissions (scope 1&2) are counterbalanced by carbon removals in our estate by 2027
-Net Zero in our full value chain (Scope 1,2&3) by 2040
Executive summary
Our approach
Our key actions
- Reduce emissions first, and use offsetting as a last resort, in line with the Science Based Targets Initiative principles.
- Set targets in line with the approach of the SBTI, and that are 1.5 degrees Paris-aligned – and support with concrete actions.
- Maximise the value of our physical assets for sustainability, including consideration of how we support the wider transition of the Thames and the UK
- Continue to reduce our fuel associated emissions through transitioning to alternative fuels and green technology.
- Reduce emissions in our supply chain through working closely with suppliers on reducing their own emissions.
- Improve our data quality and accuracy to ensure we are targeting the most impactful actions and meeting our overall objectives.
Introduction
As custodian of the tidal Thames, The Port of London Authority (PLA) remains committed to a healthy future for the river and its port activities.
To support this aim, we are committed to achieving net zero emissions in our operations, and across our value chain by 2040.
The PLA has been on an ambitious decarbonisation journey for the last ten years. This plan aims to build on these previous successes, as well as set a new trajectory to meet our goals. We first calculated the carbon footprint of our emissions in 2014, when carbon reporting was in its infancy.
This allowed us to set out on an ambitious journey to significantly reduce our carbon emissions, focusing on Scope 1&2. We did this in a variety of ways. We invested in producing solar energy on our operation sites. From January to June 2024, we generated 114MWh through solar photovoltaics – enough to power approximately 10% of our buildings’ electricity requirements.
We also took concrete steps to reduce emissions in our Scope 1 – focusing on transitioning our vessel fleet from diesel to sustainably sourced HVO (Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil). By 2023 these actions resulted in an 83% decrease in the PLA’s Scope 1&2 emissions from 2014. After ten years of successful carbon reductions, it was time to take stock of our progress and chart a new journey to reach our goals.
We only have 15 years left to reach net zero, we know we need to renew and refocus our efforts. Over the next five years, we will continue to reduce our fuel associated emissions, maximise our landholdings’ carbon removal potential, and get even better at managing our data. We will also engage with our suppliers and tenants to ensure that they are working with us to reduce Scope 3 emissions.
We believe that it’s crucial that we do this, as ports underpin the global economy and play an essential role in our everyday lives. More than 80% of global merchandise trade is transported via sea. The Port of London Authority is in a unique position, given our previous successes, to lead the way on decarbonisation for our sector.
How we define 'Net Zero'
Net-zero emissions are achieved when anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere are balanced by anthropogenic removals over a specified period. Where multiple greenhouse gas emissions are involved, the quantification of net zero emissions depends on the climate metric chosen to compare emissions of different gases (such as global warming potential, global temperature change potential, and others, as well as the chosen time horizon).
HOW WE DEFINE ‘SCOPES 1,2,3’
Scope 1 covers all direct emissions, mainly from burning fuel but also other industrial processes.
Scope 2 covers indirect emissions from the use of purchased electricity. This is reported in two ways:
- Location-based refers to the actual emissions of electricity production on the grid.
- Market-based accounts for any contractual entitlements to report lower emissions, such renewable energy certificates.
Scope 3 contains all other indirect emissions, split into several categories across the value chain
Our story so far
In 2014, the PLA implemented its first emissions reduction plan, focusing on the most material Scope 1&2 emissions for our operations. This has resulted in an 83% decrease in the PLA’s Scope 1&2 emissions in these key emission categories as shown in the graph below. These reductions have been driven by the transition of our vessel fleet to sustainable HVO, implementing energy efficiency measures, purchasing renewable electricity and investing in renewable energy production on our sites.
However, we also know that this picture of our emissions was incomplete, based on the best available information at the time of developing our plan. In 2023, we went through a full audit of our carbon footprint to bring it up to date and ensure we are capturing all our emissions going forward.
PLA Scope 1+2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Market-Based)
Measuring Emissions
Our carbon footprint is reported in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (tCO2e). This is the amount of equivalent carbon emissions generated by the main greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide etc.) each of which has a ‘Global Warming Potential’ factor that is included in the overall conversion factor. Emissions are calculated by multiplying conversion factors by activity data, such as fuel or energy consumption, resource use or mileage.
Emissions (tCO2e)= activity data × emission factor
The PLA uses the calendar year (1st January to 31st December) as the reporting period for our GHG inventory.
How we source our HVO
We are committed to purchasing sustainable HVO from reputable suppliers. All HVO supplied to PLA is ISCC verified waste derived product, free from palm oil. The Proof of Sustainability confirms the origin of raw materials, certifying that none of their products contribute to global deforestation

Our approach
2023-onwards
In 2023, we went through a full review of our methodology to bring us in line with Science Based Target initiative (SBTi) best practice guidance. This was prompted by a number of key changes to our operations including the purchase of a company by the PLA Group, the need to include full Scope 3 emissions, and an aging baseline for our carbon reporting. The key findings from this review were used to strengthen our reporting and create the actions within this action plan.
They included the key changes highlighted below:
- Updated our baseline year from 2014 to 2023 in line with best practice.
- Updated our Scope 1&2 emissions to include F-gases and all remote site energy use. • Updated our Scope 3 emissions to include purchased goods and services, capital projects, employee commuting, business travel via public transport and leased assets. Emissions from our industrial tenanted properties will be included in our 2026 update.
- Included both a market-based and location-based calculation for our Scope 2 emissions which captures our choices to purchase renewable energy, as well as the energy mix of our local supply.
- Included our fully owned subsidiary, Estuary Services Limited, as part of our Group level emissions data. ESL was purchased in 2021 and we began reporting on emissions from 2022.
This has resulted in a material change to our carbon emissions. Our new baseline which includes all emission Scopes across our full group is 9687 tCO2e – an 800% increase compared to what we reported in 2022 (primarily driven by Scope 3 emissions). This increase represents a truer calculation of our total emissions impact through our full value chain.
Scope 1 & 2 Emissions Definitions
- Gas – this covers the gas from the grid used for space and water heating.
- Liquid Fuels – this covers the fuel used in vessels, vehicles, plant, and generators that we own and operate.
- Refrigerants – this covers the fugitive emissions of refrigerant gases from installation and operation of our air conditioning systems
Scope 3 Emissions Definitions
- Purchased Goods and Services – this covers the production of goods and services we purchase that are not accounted for in other specific categories.
- Capital Goods – this covers the production of capital goods we purchase in a year.
- Fuel and Energy Indirect – this covers the production of fuels and energy we purchase (known as Well-to-Tank), as well as inefficiencies in energy distribution via the National Grid.
- Upstream and Downstream Transportation and Distribution – this covers transportation of products we purchase between our Tier 1 suppliers to our own sites by third parties. • Waste – this covers the transportation, disposal, and treatment of the waste we generate from our operations by our licensed waste contractors.
- Business Travel – this covers transportation of staff for business related activities in vehicles not owned or operated by the PLA.
- Employee Commuting and Homeworking – this covers transportation of staff between their homes and their worksites in vehicles not owned or operated by the PLA. It also optionally includes the energy use of working from home.
- Upstream Leased Assets – this covers the operation of assets leased to the PLA, which are not included in scope 1 and scope 2.
- Downstream Leased Assets - this covers the operation of assets leased out by the PLA, which are not included in scope 1 and scope 2
Our new baseline
We have updated our baseline and have readjusted our targets to be more ambitious. This recognises the substantial progress we have already made but also the urgency we feel to act as quickly as possible. The most material of change in our baseline Scope 1&2 is vessel emissions from our subsidiary company, and in Scope 3 is emissions from purchased goods and services.
Our targets
Along with updating our approach, we have updated our targets in line with SBTi guidance. Despite measuring more of our emissions, we are still on target to reach net zero by 2040. We have identified two milestone commitments, mapped our science-based trajectory, and set our interim targets to keep us on track.
Our interim trajectory and interim targets are designed to push as fast as we can on Scope 1&2 emissions as early as possible.
Our reduction actions for Scope 1&2 will leave us with a small but difficult to abate remainder (7%) of emissions by 2030. These emissions are from sources that have no clear technological solutions in the near term. However, we will continue to invest in trialling technology to reduce these emissions. We will also counterbalance these emissions through the management of our land holdings to promote carbon removal. While this cannot offset our operational emissions, we will achieve carbon neutrality of our Scope 1&2 emissions in 2027 – which is a major milestone on our path to true net zero.
Scope 3 emissions are more difficult to reduce as we have less direct ability to act. We have set our trajectory in line with the science based target initiative approach to achieving 1.5 degr
ees. As our major source of Scope 3 emissions is purchased goods and services, we will focus early on engaging with our suppliers on their own decarbonisation journeys.
Actions to Net Zero
Operational Carbon (Scope 1&2)
Most of our emissions in Scope 1&2 are from fuel used in our vessel fleet. After a successful transition to HVO in the PLA’s fleet, we have drastically reduced emissions from this source (by 83% compared to 2014). To meet our targets, we will continue the transition to HVO for the remainder of our group fleet, continue our vessel efficiencies programme, complete the roll out of the building efficiencies programme, continue our EV fleet transition, and procure 100% renewable energy for the rest of our estate.
CASE STUDY – PORT CONTROL CENTRE RETROFIT In 2023 we started a project to upgrade our Port Control Centre. Starting from first principles we used sustainability as part of our design criteria – opting for a retrofit rather than rebuild to reduce emissions. The project will reduce our energy consumption for this building by 80% through integrating a wide variety of sustainability practices such as:
- Improved insulation with a high-performance insulated cladding,
- New windows with optimized glazing to limit unwanted excess summer solar gain but maintain a level of useful winter solar gain, • High-efficiency LED lights with efficient lighting controls,
- Provision of efficient air source heat pumps for heating and cooling,
- Heat recovery on mechanical ventilation and air handling plant,
- Photovoltaic panels
Actions to Net Zero
Value Chain Carbon (Scope 3)
We are committed to reducing our Scope 3 emissions by 25% by 2030 (in line with a 1.5 trajectory). Our largest source of Scope 3 emissions is in our supply chain. Meeting our near-term target will require us to work with our supply chain on emissions reductions.
We have started trialling whole life carbon (WLC) assessments in our capital projects. For example, our Marine Centre Transformation Programme WLC assessment resulted in a refurbishment of the building instead of full rebuild.
We also recognise that we are not reporting the emissions from our downstream leased assets to a high enough level of accuracy. We will focus on engaging with tenants to understand and reduce their emissions.
Supplier Engagement Targets
62% of our Scope 3 emissions come from our purchased goods and services, and capital projects. As a result, alongside absolute carbon reductions, we have also developed supplier engagement targets. This demonstrates our commitment to work with our supply chain to reduce emissions. By 2030 we will engage with 50 Tier 1 suppliers representing 80% of our supply chain emissions.
Improving Data
We know that our performance is only as good as the data that underpins it.
That is why we are committed to improving our emissions data across all our scopes.
As part of our review, we assessed all our data sources against criteria of accuracy and quality. For example, all our data sources for our Scope 1&2 emissions have been rated as high or medium accuracy and quality – giving us a high level of confidence in our Scope 1&2 footprint.
We have a lower level of confidence over our Scope 3 data.
This is consistent with the wider industry trends as Scope 3 is third party data or estimates based on proxies. Our key areas of focus for data improvements are:
As HRO hearings conclude, PLA restates the case for safety and sustainability
Six years ago, we started a process, called a Harbour Revision Order (HRO), to update the legislative framework that governs the Port of London Authority’s (PLA) operations, which is almost 60 years old. This week the final stage of the inquiry closes.
The Port of London is the UK’s biggest port – bringing more goods into the country than any other – and the country’s busiest inland waterway.
The Port of London Authority is a statutory harbour authority and a trust port; accountable to the Department for Transport, with responsibility for safety and conservancy through London, Kent and Essex, out to the North Sea. There are over 100 trust ports in the UK, ranging from other large commercial ports to small local harbours. Like other trust ports, the PLA has no shareholders. All of the revenues it generates, the significant majority of which derive from facilitating the safe delivery of commercial trade, are used and invested for the benefit of its customers, stakeholders and the environment.
The PLA’s chair and a number of its non-executive directors are appointed by the Secretary of State for Transport. The PLA has a particular responsibility for discharging the Port Marine Safety Code.
The PLA’s 1968 Act has a cross-cutting statutory duty to protect the Thames environment (“conservancy”), and there are around 140 pieces of national environmental legislation which cover its activities.
The PLA adopts a proactive approach to environmental improvement, as evidenced in the Clean Thames Manifesto, and Net Zero Plans. The PLA does not consider that additional environmental provisions are necessary in the PLA Act, given this existing body of law, and as it would not be desirable or practical to duplicate the functions of national environmental regulators such as the Marine Management Organisation (MMO), Environment Agency (EA) or Natural England (NE).
Since 2019, the PLA and the Marine Management Organisation, the body appointed by the Department of Transport to run the HRO process, have been reviewing, consulting and seeking evidence on the PLA’s proposals. The process has been highly consultative, with all interests and voices given space and time to make their case.
We have heard from many organisations supporting modernisation, and a large majority of the PLA’s stakeholders have not raised any objections. For example, there are no outstanding objections from any local authorities, the Greater London Authority (GLA), Natural England or the Environment Agency; nor from any port terminals, freight or passenger vessel operators, recreational clubs or national environmental charities. But we know some others have concerns, whether about the proposed measures in the HRO or issues unconnected to the HRO.
One example is homeowners whose properties have balconies which hang out over the tidal Thames. For homes enjoying this benefit, we levy a fee, as set out in PLA’s legislation, and in total, there are just over 200 balconies affected, paying on average around £950 per year + VAT. Taken together balcony charges provide 0.3% of the PLA’s total revenues. There is nothing in the HRO proposals related to this, but campaigners have taken the chance to make their voices heard and we have listened. On this issue, as all others, we are committed to being fair and reasonable so we have invited the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors to review our approach and make any recommendations.
The reason the PLA brought forward the proposals in the HRO was to make a number of necessary changes to help us keep ships, people, and the environment safe.
Examples include being able to improve navigational lighting, so boats move safely on the river; ensure grab chains and escape ladders are installed where needed; and secure powers to intervene if party boats or similar are found to be overcrowded.
As the UK’s biggest port, the PLA must be able to step into the future with a modern legislative framework to support a thriving Thames with activities operating safely and sustainably.
Related content

Location: London/Gravesend Remuneration: £28,971 per annum for a commitment of up to 24 days per...


Update on fees for balconies overhanging the River Thames
There have been ongoing discussions relating to the PLA’s licence fees for residential balconies which overhang the River Thames. These are fees required by the PLA under its legislation, set at a level informed by local property market conditions. Balcony owners have the chance to discuss or challenge proposed changes in fees, which happen periodically to reflect changes in the property market. There is an established arbitration regime to assist in cases of unresolved dispute.
We continue to be open in our approach of listening to the interests of all parties and are committed to an approach which is fair and reasonable to property owners, reflecting market rates and practices in other parts of the residential property sector. We are also keen to reach a broader consensus across those with residential balconies that overhang the Thames on what is a fair and reasonable approach.
To that end, we have written to the President of the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS) asking him to appoint an independent surveyor to (i) examine and report on the PLA’s current fee charging methodology for residential balconies; and (ii) provide the PLA’s Board with recommended options for setting licence fees in the future. This review will need to take into account requirements under the Port of London Act 1968.
While this review is ongoing, we propose to delay any upcoming five-year rent reviews and pause discussions on any ongoing rent reviews and challenges.
We will publish the conclusions of this work to provide transparency and predictability for both the PLA and licensees going forwards.
Related content

Location: London/Gravesend Remuneration: £28,971 per annum for a commitment of up to 24 days per...


Trial of CSO Warning Lights
Consultation C01-25 / Closed Saturday 19th April
CONSULTATION STATEMENT: C01-25: Trial of CSO Warning Lights
This consultation ran from 20/03/2025 to 19/04/2025. The below statement has been provided to summarise the Port of London Authority’s response.
Following the consultation on the location and characteristics of warning lights at Tideway Tunnel Combined Sewer Outfall (CSO) sites along the Thames, no responses were received. Accordingly, the PLA, Tideway and their contractors - NASH Maritime and Beckett Rankine - have taken this as an indication of general acceptance of the appropriateness of the proposed lights. These lights will therefore be brought into operation at the relevant sites in due course, with details to be communicated via Notice to Mariners.
1. Introduction
1.1. The PLA and the Tideway Tunnel Project team invite you to share your feedback on this trial (see Proposal) and in particular your views on the location and visibility of lights for river users.
1.2. This consultation and trial affect the following areas:
A. Chelsea Embankment Foreshore
B. Victoria Embankment Foreshore
C. Heathwall Pumping Station
D. Albert Embankment Foreshore
2. The Consultation Process
Affected Parties
2.1. This consultation is directed towards river users who frequently or occasionally navigate in or near the areas described in 1.2.
Consultation Duration
2.2. This consultation opens on 20th March 2025 and will last for 30 days including the trial period. It will close on 19th April 2025 at 23:59.
Conclusion
2.3. The information you submit will be made available to other parties and responses to this consultation are anonymous.
2.4. We appreciate all responses to our consultations however, as responses to this consultation are anonymous, we are unable to respond directly to respondents. We will issue a Consultation Statement once responses have been reviewed.
3. Responses to this Consultation
3.1. Reponses to the consultation should be sent so that they are received no later than the closing date detailed in 2.2.
3.2. Unlike previous navigational consultations from the PLA, responses to this consultation may only be submitted by using the online form. We regret that we cannot accept responses in any other format.
3.3. To access the form, follow the link or scan the QR code below. Please note that this form will only accept responses during the time period described in 2.2 Consultation Duration.
4. Proposal
4.1. Mariners are advised that for a period of five days from 20th- 24th March 2025 the Tideway Tunnel Project team will be trialling Combined Sewer Outfall (CSO) warning lights at their sites at Chelsea Embankment, Albert Embankment, Heathwall Pumping Station and Victoria Embankment Foreshore.
4.2. These warning lights will be used to indicate to mariners when a CSO is discharging. This is a trial only and these lights do not currently indicate an active CSO discharging. Separate NTMs will be published for each site once it comes online.
4.3. Mariners should note that the trial light at Chelsea Embankment will be in addition to the operational light described in NTM 23-25, which should be followed.
4.4. The approximate location of the trial lights on each site is shown on the following chartlets.
Chelsea Embankment Foreshore
Victoria Embankment Foreshore
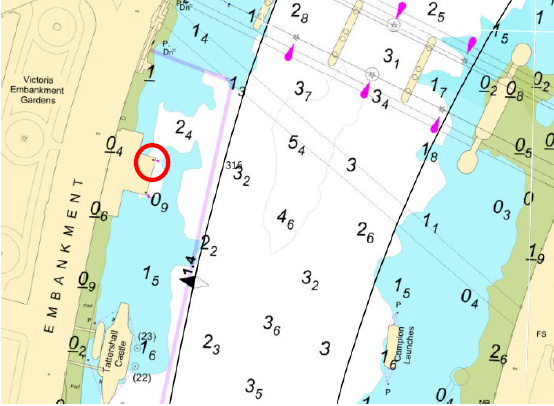
Heathwall Pumping Station
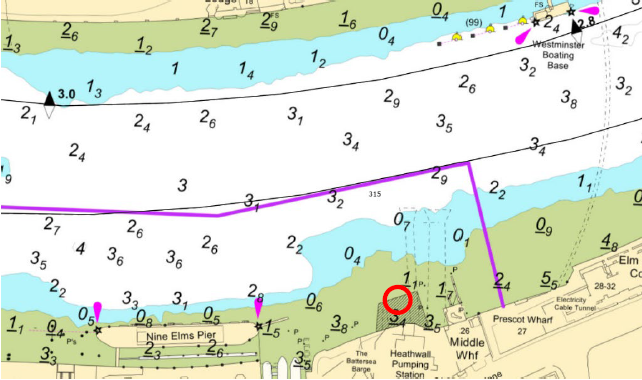
Albert Embankment Foreshore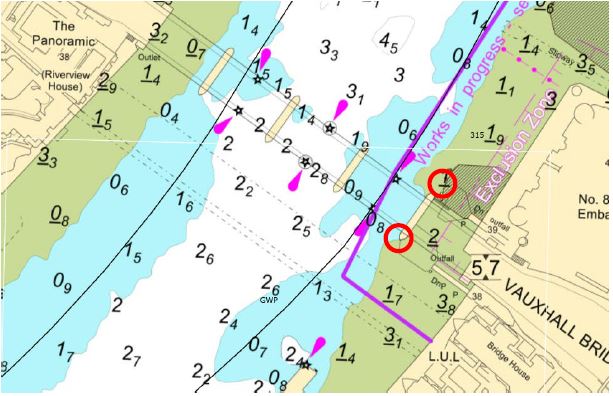
4.5. The lights will be mounted on masts at each site and will display two vertical yellow lights alternately flashing ½ second over a 1 second period. Albert site will also have a repeater light located on Vauxhall Bridge facing upriver between arches 4 &5, as shown on the chartlet above.
A Hydrographer’s path from study to the PLA

Since 1999, the PLA’s Hydrography team has worked in partnership with UCL Civil, Environmental and Geomatics Engineering (CEGE) to deliver the internationally accredited 'MSc in Geospatial Science, Hydrographic Surveying' course, supporting the education of future hydrographic surveyors from around the world.
Originally from Grays, Essex, PLA Hydrographic Surveyor, Tom Ford, decided to invest in the course with an ambition to work for the Port of London. Tom graduated with his 'MSc in Geospatial Science, Hydrographic Surveying' in 2016 before joining the Hydrographic team at Forth Ports in Edinburgh for five and a half years. He then returned to his roots by the Thames, achieving his goal of working in the world-class Hydro team at the PLA.
Since then, Tom has been supporting the UCL course, which he says gives him a chance to feedback into the latest cohort of students, demonstrate the advantages of the advanced multibeam technology which is on the PLA vessels, and gain from the high engineering and science that is happening in the background.
Although as Tom quips: “It’s great that the students can benefit from the latest and greatest in tech and tools but the very first thing we teach the international students, when they get onboard our boats, is arguably the most important task of all: to put the kettle on. Long days on the water mean tea and biscuits are an essential part of Hydrographic Surveying!”

Related content

Location: London/Gravesend Remuneration: £28,971 per annum for a commitment of up to 24 days per...


Harbour Revision Order (HRO) Statement
The Port of London (PLA), the UK’s biggest port and busiest inland waterway, welcomes the world’s most modern vessels, is a hub for environmental innovation and home to river communities, and is investing in future technology and resilience, yet we are covered by legislation last significantly updated nearly 60 years ago.
In 2019, the PLA proposed a Harbour Revision Order (HRO), the mechanism through which we can modernise the Port of London Act (1968). The HRO includes a range of updates, from a definition for autonomous vessels and adding email as a form of communication, to removing references to customs roles and responsibilities that haven’t been performed by the PLA for many years. We’ve also refined definitions around river works licenses, charting and dredging, and included references to more recent environmental legislation and agencies.
In response to an informal consultation on the proposed HRO, we heard from 50 stakeholders with a wide range of interests, including residents and houseboat owners, terminal operators and other port businesses. Their feedback was reflected in the next iteration of the HRO which the Marine Management Organisation (MMO), the body appointed by the Department for Transport to oversee HROs, consulted on in 2021. We were pleased that, through this extensive process of engagement and consultation, the vast majority of questions were resolved. In 2024, the MMO decided to hold a public inquiry, starting this week, to make sure any remaining concerns could be heard and fully considered before the HRO is finally signed off. Over the next few weeks, the inquiry will have an opportunity to hear from PLA colleagues and interested parties on a range of different matters.
We know – through our public meetings, stakeholder fora and regular correspondence – that the tidal Thames is incredibly important in so many people’s lives, and I’m always impressed by the time, energy and commitment our stakeholders put into representing the variety of interests associated with the river. I’m glad that during the inquiry they will be able to represent their views directly to the MMO. Through this, we can arrive at a final HRO that protects and improves the tidal Thames for all, enabling us to build resilience, as modern operations and cutting-edge technology accelerate the changes in trade and traffic, as well as the energy transition in the UK.
Related content

Location: London/Gravesend Remuneration: £28,971 per annum for a commitment of up to 24 days per...


Sailing toward success: PLA welcomes four new Trainee Pilots
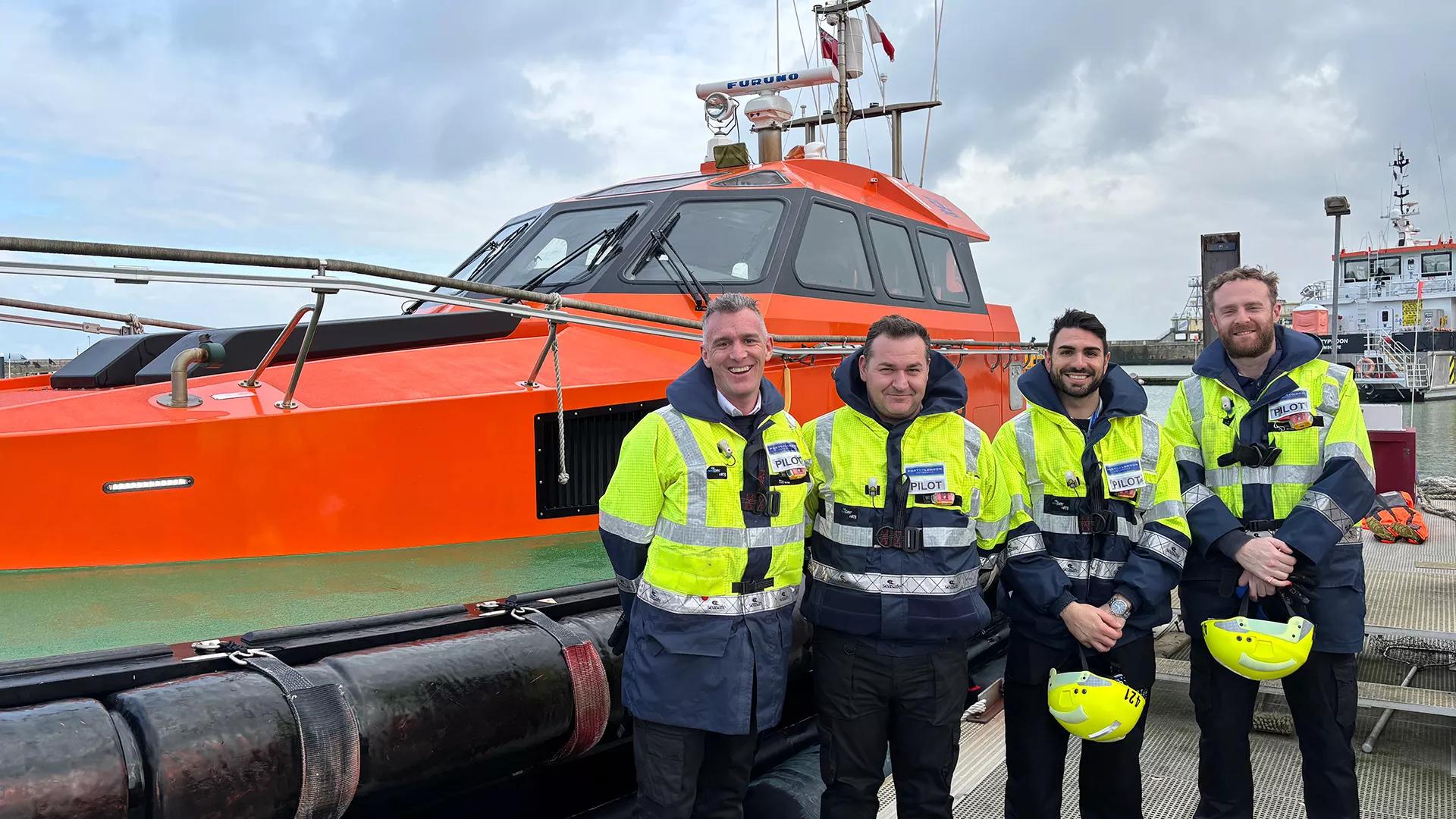

Our newest recruits, (L-R) Fraser Matthew, David Shaw, Carmelo Giannone, and Robert Hoyland, bring extensive maritime experience from a range of backgrounds within the shipping industry. As they progress through their intensive training, they will refine the skills required to safely guide vessels through the river’s busy and often demanding waters.
Fraser Matthew – Kirkcaldy, Fife
Fraser has spent the last 19 years at sea, beginning his career on cruise ships as a Cadet and Junior Officer before moving to ro-ro passenger ferries around the UK coast. Over the past decade, he has served as Chief Officer and Master on routes across the Irish Sea, the Scottish Islands, and most recently the English Channel between Dover and Calais.
Fraser pursued a career at sea because he wanted to drive ships, finding it both the most challenging and rewarding aspect of the job. Becoming a PLA Pilot offers him the opportunity to handle a wide variety of vessels on one of the world’s most famous waterways. He is looking forward to working with and learning from a team with diverse sea-going and non-seagoing backgrounds—though he certainly won’t miss battling against South-Westerly gales!
David Shaw – Falmouth, Cornwall
David began his maritime career at 17, joining the Royal Navy as a Rating in 2001 before transitioning to the Merchant Navy in 2005 as a Deck Cadet. He initially worked on container ships and bulk carriers before gaining experience on dredgers and anchor handlers. He later moved into the passenger sector, working with Saga Cruises from 2011 to 2016, followed by Thomson Cruises (later Marella Cruises) from 2016 to 2024, leaving as Staff Captain in January 2024. Since then, he has served as Mate at Red Funnel Ferries in Southampton.
David was drawn to the PLA for its diverse port operations and the challenge of handling different vessels. He was also motivated by the trust port’s purpose-driven approach, which aligns with his values. After 23 years at sea, he is eager to settle down and spend more time with family while taking on a role that demands adaptability and quick thinking.
Carmelo Giannone – Sicily, Italy
Carmelo began his career with Costa Cruises in 2012, progressing from Cadet Officer to First Officer during his 11-year tenure. He then served as First Officer on Princess Cruises.
Passionate about ship handling, Carmelo is eager to apply his maritime experience in a new, challenging environment. He looks forward to manoeuvring different types of vessels and expanding his skill set on the River Thames.
Robert Hoyland – Sheffield, Yorkshire
Robert spent four years as a Navigation Officer on 90m general cargo vessels before serving as Chief Officer on the same vessels for over two years. In August 2024, he achieved his Master’s Unlimited license.
Robert has always viewed pilots as some of the most skilled and professional individuals in the maritime industry. With a passion for ship handling and close-quarters navigation, he is eager to develop his expertise on the River Thames and become an expert in its challenging waters.
Related content

Location: London/Gravesend Remuneration: £28,971 per annum for a commitment of up to 24 days per...


Discover



